After install fedora 17 into my friend computer, My desktop gets your turn.
I follow my classic fedora installation method.
- Download install DVD x86_64 version iso image.
- Burn a blank DVD
- Boot my computer from the DVD
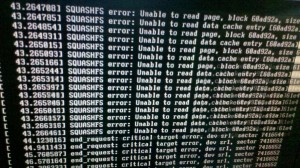
these are my normal steps but my boot DVD shoa lot of errors like:
SQUASHFS error: Unable to read page, block xxxxxxxF, size xxxF
I read some info from forums and they say that the problem was with the dvd, Because after install fedora in my desktop I was installed Hasefroch 7 and burned Fedora ISO in the same computer.
After Downloaded Sha256 for windows and check that I have the correct image, i go to bed and leave the computer checking a new recorder DVD.
When I get up I observer tat new DVD has errors too, so i decided to download a live cd iso and try with live CD, this method works and i could install fedora but i saw a small number of errors but it was thinking the live cd too small for support everything. so i decide install my system from the live cd hopping that errors disappears at first boot.
After install a bad behavior appear in the screen and system appears to frozen in moments with unexpected X restarts. I decide to check running process using top et voila. My Phenom computer only has one processor working 🙁 . After that I remember that when change the hard disk some wires from the pow source stopped the CPU fan for a moment, 20 secs approx, a disaster has coming i burn my cpu and need to buy a new processor, but when i reboot on haseforch saw four cores working, that not was a CPU problem so I check the dmesg output.
[ 0.006467] ACPI: Core revision 20120111 [ 0.009031] ftrace: allocating 22596 entries in 89 pages [ 0.017650] ..TIMER: vector=0x30 apic1=0 pin1=2 apic2=-1 pin2=-1 [ 0.028157] CPU0: AMD Phenom(tm) 9850 Quad-Core Processor stepping 03 [ 0.028998] Performance Events: AMD PMU driver. [ 0.028998] ... version: 0 [ 0.028998] ... bit width: 48 [ 0.028998] ... generic registers: 4 [ 0.028998] ... value mask: 0000ffffffffffff [ 0.028998] ... max period: 00007fffffffffff [ 0.028998] ... fixed-purpose events: 0 [ 0.028998] ... event mask: 000000000000000f [ 0.028998] NMI watchdog enabled, takes one hw-pmu counter. [ 0.028998] Booting Node 0, Processors #1 [ 0.028998] smpboot cpu 1: start_ip = 93000 [ 6.975648] CPU1: Not responding. [ 6.976466] #2 [ 6.976475] smpboot cpu 2: start_ip = 93000 [ 14.279079] CPU2: Not responding. [ 14.281137] #3 [ 14.281146] smpboot cpu 3: start_ip = 93000 [ 21.143977] CPU3: Not responding. [ 21.144993] Brought up 1 CPUs [ 21.145004] Total of 1 processors activated (5022.87 BogoMIPS). [ 21.147104] devtmpfs: initialized [ 21.147356] PM: Registering ACPI NVS region at cfcf0000 (12288 bytes)
I try changing kernel boot parameters without acpi with NOACPI and a lot of things and every time that my computer reboot my Linux only show one core.
Finally i found the guilty element it doesn’t was the CPU it was the motherboard
 I update the bios using the last version but it doesn’t work, finally I download a BIOS beta version , mb_bios_ga-ma785gm-us2h_f12a, from gigabyte web page and it works.
I update the bios using the last version but it doesn’t work, finally I download a BIOS beta version , mb_bios_ga-ma785gm-us2h_f12a, from gigabyte web page and it works.
[ 0.026770] CPU0: AMD Phenom(tm) 9850 Quad-Core Processor stepping 03 [ 0.026998] Performance Events: AMD PMU driver. [ 0.026998] ... version: 0 [ 0.026998] ... bit width: 48 [ 0.026998] ... generic registers: 4 [ 0.026998] ... value mask: 0000ffffffffffff [ 0.026998] ... max period: 00007fffffffffff [ 0.026998] ... fixed-purpose events: 0 [ 0.026998] ... event mask: 000000000000000f [ 0.026998] NMI watchdog enabled, takes one hw-pmu counter. [ 0.026998] Booting Node 0, Processors #1 [ 0.026998] smpboot cpu 1: start_ip = 93000 [ 0.038014] NMI watchdog enabled, takes one hw-pmu counter. [ 0.038094] #2 [ 0.038095] smpboot cpu 2: start_ip = 93000 [ 0.050011] NMI watchdog enabled, takes one hw-pmu counter. [ 0.050083] #3 [ 0.050084] smpboot cpu 3: start_ip = 93000 [ 0.062009] NMI watchdog enabled, takes one hw-pmu counter. [ 0.062032] Brought up 4 CPUs [ 0.062034] Total of 4 processors activated (20091.79 BogoMIPS).
Now all the cores are available. Screen doesn’t works yet and I’m downloading a new DVD copy because i don’t like liveCD install.
Enjoy